注意
跳至結尾下載完整的範例程式碼。或透過 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
斑點偵測#
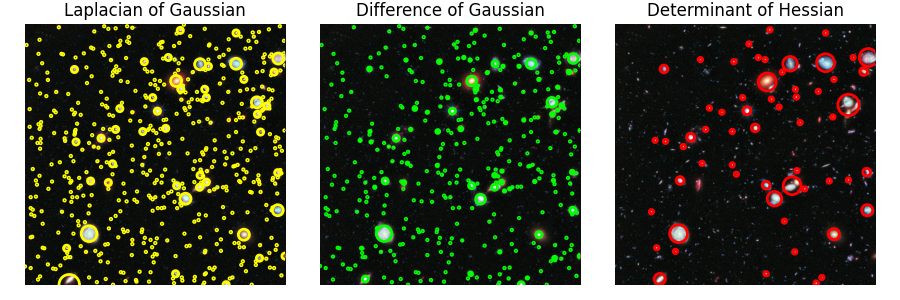
斑點是影像中明亮背景上的暗區域或暗背景上的明亮區域。在此範例中,使用 3 種演算法偵測斑點。此處使用的影像為哈伯極深空場。影像中的每個亮點都是一顆恆星或星系。
高斯拉普拉斯 (LoG)#
這是最準確且最慢的方法。它計算具有連續增加標準差的高斯影像的拉普拉斯算子,並將它們堆疊在一個立方體中。斑點是此立方體中的局部最大值。由於卷積期間較大的核心大小,偵測較大的斑點速度會特別慢。僅偵測暗背景上的明亮斑點。有關使用方法,請參閱 skimage.feature.blob_log()。
高斯差分 (DoG)#
這是 LoG 方法的更快近似值。在此情況下,影像會以增加的標準差模糊化,並且兩個連續模糊影像之間的差異會堆疊在一個立方體中。此方法與 LoG 方法在偵測較大斑點方面面臨相同的缺點。斑點再次被假設為暗背景上的明亮斑點。有關使用方法,請參閱 skimage.feature.blob_dog()。
黑塞行列式 (DoH)#
這是最快的方法。它透過在影像黑塞行列式矩陣中尋找最大值來偵測斑點。由於內部實作使用盒狀濾波器而非卷積,因此偵測速度與斑點的大小無關。偵測暗背景上的明亮斑點以及明亮背景上的暗斑點。缺點是無法準確偵測小斑點(<3px)。有關使用方法,請參閱 skimage.feature.blob_doh()。
from math import sqrt
from skimage import data
from skimage.feature import blob_dog, blob_log, blob_doh
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image = data.hubble_deep_field()[0:500, 0:500]
image_gray = rgb2gray(image)
blobs_log = blob_log(image_gray, max_sigma=30, num_sigma=10, threshold=0.1)
# Compute radii in the 3rd column.
blobs_log[:, 2] = blobs_log[:, 2] * sqrt(2)
blobs_dog = blob_dog(image_gray, max_sigma=30, threshold=0.1)
blobs_dog[:, 2] = blobs_dog[:, 2] * sqrt(2)
blobs_doh = blob_doh(image_gray, max_sigma=30, threshold=0.01)
blobs_list = [blobs_log, blobs_dog, blobs_doh]
colors = ['yellow', 'lime', 'red']
titles = ['Laplacian of Gaussian', 'Difference of Gaussian', 'Determinant of Hessian']
sequence = zip(blobs_list, colors, titles)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(9, 3), sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax = axes.ravel()
for idx, (blobs, color, title) in enumerate(sequence):
ax[idx].set_title(title)
ax[idx].imshow(image)
for blob in blobs:
y, x, r = blob
c = plt.Circle((x, y), r, color=color, linewidth=2, fill=False)
ax[idx].add_patch(c)
ax[idx].set_axis_off()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
腳本總執行時間: (0 分鐘 5.736 秒)
