注意
前往結尾下載完整範例程式碼。或透過 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
Max-tree#
max-tree 是影像的階層式表示法,是大量形態學濾波器的基礎。
如果我們對影像套用閾值運算,我們會獲得一個包含一個或多個連通元件的二值影像。如果我們套用較低的閾值,則較高閾值的所有連通元件都包含在較低閾值的連通元件中。這自然定義了一個嵌套元件的階層,可以用樹狀結構表示。每當通過閾值 t1 獲得的連通元件 A 包含在通過閾值 t1 < t2 獲得的元件 B 中時,我們就說 B 是 A 的父項。產生的樹狀結構稱為元件樹。max-tree 是此類元件樹的簡潔表示。[1]、[2]、[3]、[4]
在本範例中,我們給出 max-tree 是什麼的直覺。
參考文獻#
在我們開始之前:一些輔助函式
def plot_img(ax, image, title, plot_text, image_values):
"""Plot an image, overlaying image values or indices."""
ax.imshow(image, cmap='gray', aspect='equal', vmin=0, vmax=np.max(image))
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_xticks([])
for x in np.arange(-0.5, image.shape[0], 1.0):
ax.add_artist(
Line2D((x, x), (-0.5, image.shape[0] - 0.5), color='blue', linewidth=2)
)
for y in np.arange(-0.5, image.shape[1], 1.0):
ax.add_artist(Line2D((-0.5, image.shape[1]), (y, y), color='blue', linewidth=2))
if plot_text:
for i, j in np.ndindex(*image_values.shape):
ax.text(
j,
i,
image_values[i, j],
fontsize=8,
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
color='red',
)
return
def prune(G, node, res):
"""Transform a canonical max tree to a max tree."""
value = G.nodes[node]['value']
res[node] = str(node)
preds = [p for p in G.predecessors(node)]
for p in preds:
if G.nodes[p]['value'] == value:
res[node] += f", {p}"
G.remove_node(p)
else:
prune(G, p, res)
G.nodes[node]['label'] = res[node]
return
def accumulate(G, node, res):
"""Transform a max tree to a component tree."""
total = G.nodes[node]['label']
parents = G.predecessors(node)
for p in parents:
total += ', ' + accumulate(G, p, res)
res[node] = total
return total
def position_nodes_for_max_tree(G, image_rav, root_x=4, delta_x=1.2):
"""Set the position of nodes of a max-tree.
This function helps to visually distinguish between nodes at the same
level of the hierarchy and nodes at different levels.
"""
pos = {}
for node in reversed(list(nx.topological_sort(canonical_max_tree))):
value = G.nodes[node]['value']
if canonical_max_tree.out_degree(node) == 0:
# root
pos[node] = (root_x, value)
in_nodes = [y for y in canonical_max_tree.predecessors(node)]
# place the nodes at the same level
level_nodes = [y for y in filter(lambda x: image_rav[x] == value, in_nodes)]
nb_level_nodes = len(level_nodes) + 1
c = nb_level_nodes // 2
i = -c
if len(level_nodes) < 3:
hy = 0
m = 0
else:
hy = 0.25
m = hy / (c - 1)
for level_node in level_nodes:
if i == 0:
i += 1
if len(level_nodes) < 3:
pos[level_node] = (pos[node][0] + i * 0.6 * delta_x, value)
else:
pos[level_node] = (
pos[node][0] + i * 0.6 * delta_x,
value + m * (2 * np.abs(i) - c - 1),
)
i += 1
# place the nodes at different levels
other_level_nodes = [
y for y in filter(lambda x: image_rav[x] > value, in_nodes)
]
if len(other_level_nodes) == 1:
i = 0
else:
i = -len(other_level_nodes) // 2
for other_level_node in other_level_nodes:
if (len(other_level_nodes) % 2 == 0) and (i == 0):
i += 1
pos[other_level_node] = (
pos[node][0] + i * delta_x,
image_rav[other_level_node],
)
i += 1
return pos
def plot_tree(graph, positions, ax, *, title='', labels=None, font_size=8, text_size=8):
"""Plot max and component trees."""
nx.draw_networkx(
graph,
pos=positions,
ax=ax,
node_size=40,
node_shape='s',
node_color='white',
font_size=font_size,
labels=labels,
)
for v in range(image_rav.min(), image_rav.max() + 1):
ax.hlines(v - 0.5, -3, 10, linestyles='dotted')
ax.text(-3, v - 0.15, f"val: {v}", fontsize=text_size)
ax.hlines(v + 0.5, -3, 10, linestyles='dotted')
ax.set_xlim(-3, 10)
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_axis_off()
影像定義#
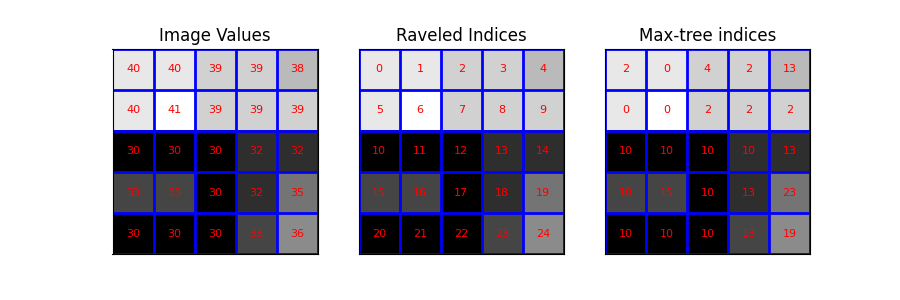
我們定義一個小的測試影像。為了清楚起見,我們選擇一個範例影像,其中影像值不會與索引混淆(不同的範圍)。
Max-tree#
接下來,我們計算此影像的 max-tree。影像的 max-tree
影像繪圖#
然後,我們視覺化影像及其展開的索引。具體來說,我們繪製具有以下覆蓋層的影像:- 影像值 - 展開的索引(用作像素識別碼) - max_tree 函式的輸出
# raveled image
image_rav = image.ravel()
# raveled indices of the example image (for display purpose)
raveled_indices = np.arange(image.size).reshape(image.shape)
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3, sharey=True, figsize=(9, 3))
plot_img(ax1, image - image.min(), 'Image Values', plot_text=True, image_values=image)
plot_img(
ax2,
image - image.min(),
'Raveled Indices',
plot_text=True,
image_values=raveled_indices,
)
plot_img(ax3, image - image.min(), 'Max-tree indices', plot_text=True, image_values=P)
視覺化閾值運算#
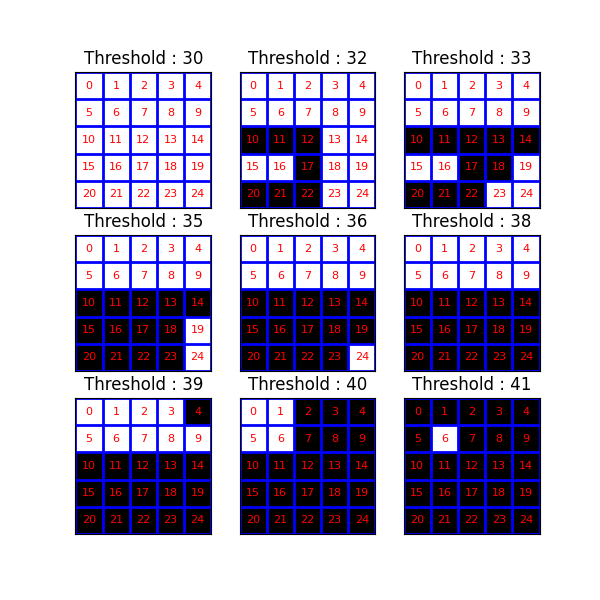
現在,我們研究一系列閾值運算的結果。元件樹(和 max-tree)提供了不同級別連通元件之間包含關係的表示法。
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, sharey=True, sharex=True, figsize=(6, 6))
thresholds = np.unique(image)
for k, threshold in enumerate(thresholds):
bin_img = image >= threshold
plot_img(
axes[(k // 3), (k % 3)],
bin_img,
f"Threshold : {threshold}",
plot_text=True,
image_values=raveled_indices,
)
Max-tree 繪圖#
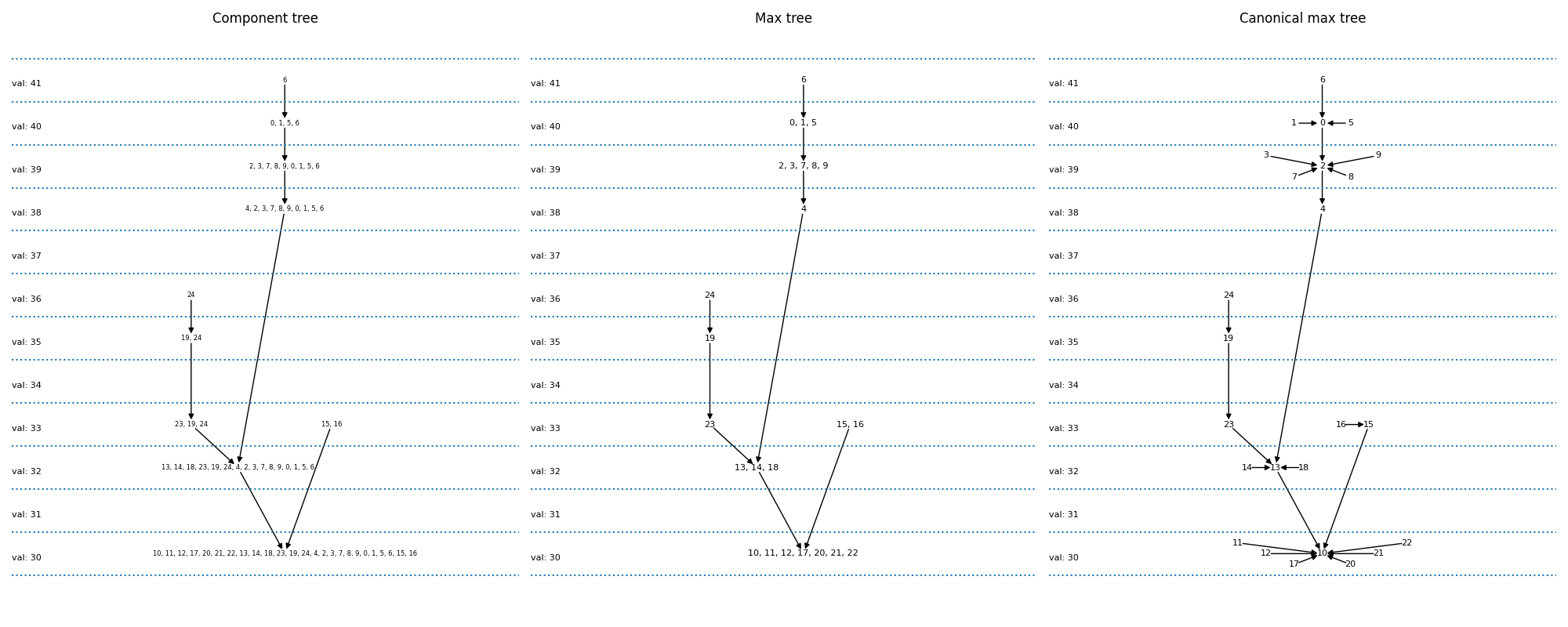
現在,我們繪製元件樹和 max-tree。元件樹將所有可能的閾值運算產生的不同像素集相互關聯。如果一個層級的元件包含在較低層級的元件中,則圖形中會有一個箭頭。max-tree 只是像素集的不同編碼方式。
元件樹:像素集被明確寫出。例如,我們看到 {6}(在 41 處套用閾值的結果)是 {0, 1, 5, 6}(在 40 處套用閾值)的父項。
max-tree:只有在此層級進入集合的像素才被明確寫出。因此,我們將寫出 {6} -> {0,1,5} 而不是 {6} -> {0, 1, 5, 6}
正規最大樹 (canonical max-treeL) 是我們實作所提供的表示法。在此,每個像素都是一個節點。數個像素的連通元件由其中一個像素代表。因此,我們將 {6} -> {0,1,5} 取代為 {6} -> {5},{1} -> {5},{0} -> {5}。這使我們能夠用一個影像(頂列,第三欄)來表示圖形。
# the canonical max-tree graph
canonical_max_tree = nx.DiGraph()
canonical_max_tree.add_nodes_from(S)
for node in canonical_max_tree.nodes():
canonical_max_tree.nodes[node]['value'] = image_rav[node]
canonical_max_tree.add_edges_from([(n, P_rav[n]) for n in S[1:]])
# max-tree from the canonical max-tree
nx_max_tree = nx.DiGraph(canonical_max_tree)
labels = {}
prune(nx_max_tree, S[0], labels)
# component tree from the max-tree
labels_ct = {}
total = accumulate(nx_max_tree, S[0], labels_ct)
# positions of nodes : canonical max-tree (CMT)
pos_cmt = position_nodes_for_max_tree(canonical_max_tree, image_rav)
# positions of nodes : max-tree (MT)
pos_mt = dict(zip(nx_max_tree.nodes, [pos_cmt[node] for node in nx_max_tree.nodes]))
# plot the trees with networkx and matplotlib
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3, sharey=True, figsize=(20, 8))
plot_tree(
nx_max_tree,
pos_mt,
ax1,
title='Component tree',
labels=labels_ct,
font_size=6,
text_size=8,
)
plot_tree(nx_max_tree, pos_mt, ax2, title='Max tree', labels=labels)
plot_tree(canonical_max_tree, pos_cmt, ax3, title='Canonical max tree')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
腳本總執行時間: (0 分鐘 1.556 秒)
