注意
前往結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。或透過 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
形態學濾波#
形態學影像處理是一組非線性操作,與影像中特徵的形狀或形態相關,例如邊界、骨架等。在任何給定的技術中,我們使用稱為結構元素的小形狀或範本探測影像,該結構元素定義像素周圍的感興趣區域或鄰域。
在本文件中,我們概述了以下基本形態學操作
侵蝕
膨脹
開運算
閉運算
白色頂帽
黑色頂帽
骨架化
凸包
首先,讓我們使用 io.imread 載入影像。請注意,形態學函數僅適用於灰階或二元影像,因此我們設定 as_gray=True。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage.util import img_as_ubyte
orig_phantom = img_as_ubyte(data.shepp_logan_phantom())
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(orig_phantom, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
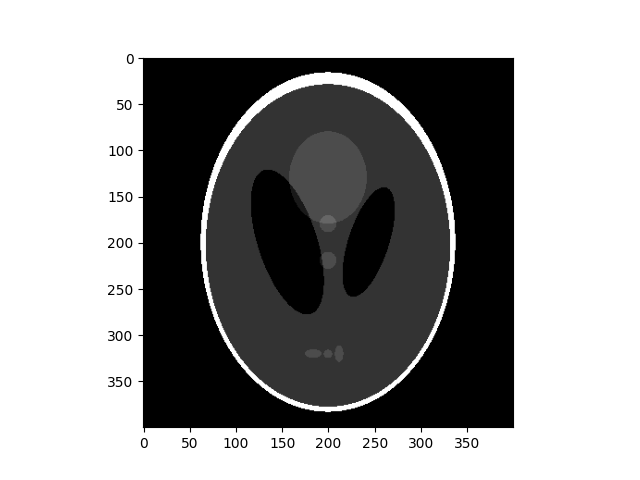
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f036a3059a0>
我們也來定義一個用於繪製比較的方便函數
def plot_comparison(original, filtered, filter_name):
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(8, 4), sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax1.imshow(original, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax1.set_title('original')
ax1.set_axis_off()
ax2.imshow(filtered, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax2.set_title(filter_name)
ax2.set_axis_off()
侵蝕#
形態學 侵蝕 將 (i, j) 處的像素設定為以 (i, j) 為中心的所有鄰域像素的最小值。傳遞給 侵蝕 的結構元素 足跡 是一個布林值陣列,用於描述此鄰域。在下面,我們使用 disk 建立一個圓形結構元素,我們將其用於以下大多數範例。
from skimage.morphology import erosion, dilation, opening, closing, white_tophat
from skimage.morphology import black_tophat, skeletonize, convex_hull_image
from skimage.morphology import disk
footprint = disk(6)
eroded = erosion(orig_phantom, footprint)
plot_comparison(orig_phantom, eroded, 'erosion')
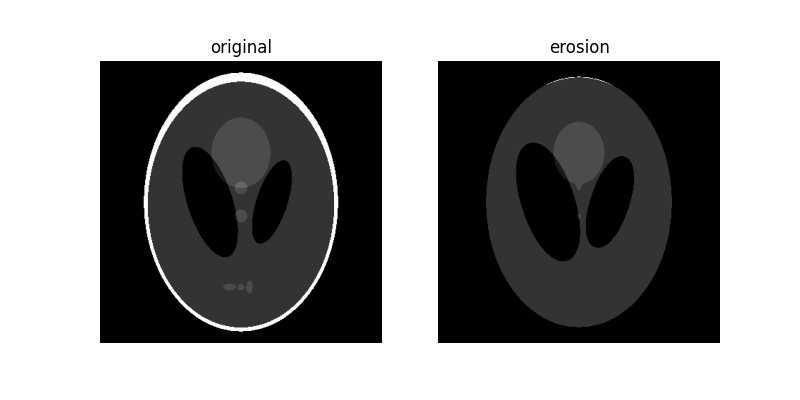
請注意,隨著我們增加磁碟的大小,影像的白色邊界如何消失或被侵蝕。另請注意中心兩個黑色橢圓形的大小增加,以及影像下半部分 3 個淺灰色色塊的消失。
膨脹#
形態學 膨脹 將 (i, j) 處的像素設定為以 (i, j) 為中心的所有鄰域像素的最大值。膨脹會擴大明亮區域並縮小黑暗區域。
dilated = dilation(orig_phantom, footprint)
plot_comparison(orig_phantom, dilated, 'dilation')
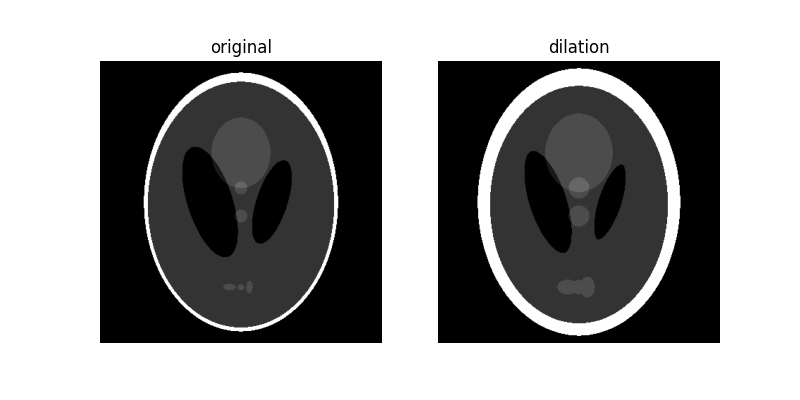
請注意,隨著我們增加磁碟的大小,影像的白色邊界如何加厚或膨脹。另請注意中心兩個黑色橢圓形的大小減小,以及中心淺灰色圓形和影像下半部分 3 個色塊的加厚。
開運算#
影像的形態學 開運算 定義為先侵蝕再膨脹。開運算可以移除小的明亮斑點(即「鹽」),並連接小的黑暗裂縫。
opened = opening(orig_phantom, footprint)
plot_comparison(orig_phantom, opened, 'opening')
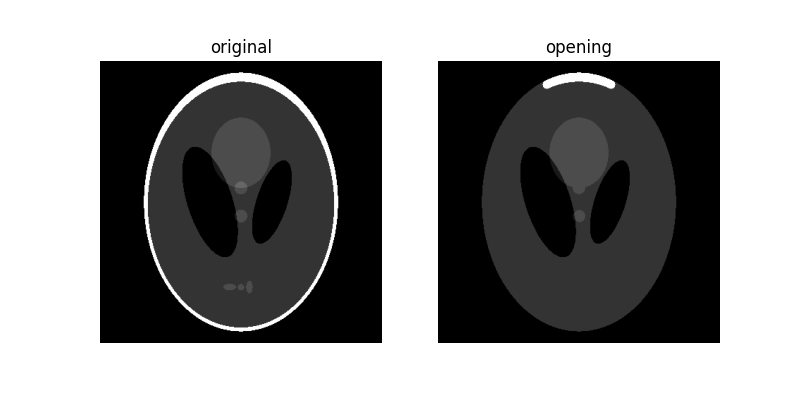
由於 開運算 影像從侵蝕操作開始,因此小於結構元素的明亮區域會被移除。隨後的膨脹操作可確保大於結構元素的明亮區域保留其原始大小。請注意,中心的亮暗形狀如何保留其原始厚度,但底部的 3 個較淺的色塊被完全侵蝕。外部白色環突出顯示了大小依賴性:比結構元素薄的環部分被完全擦除,而頂部較厚的區域保留其原始厚度。
閉運算#
影像的形態學 閉運算 定義為先膨脹再侵蝕。閉運算可以移除小的黑暗斑點(即「胡椒」),並連接小的明亮裂縫。
為了更清楚地說明這一點,讓我們在白色邊框上新增一個小裂縫
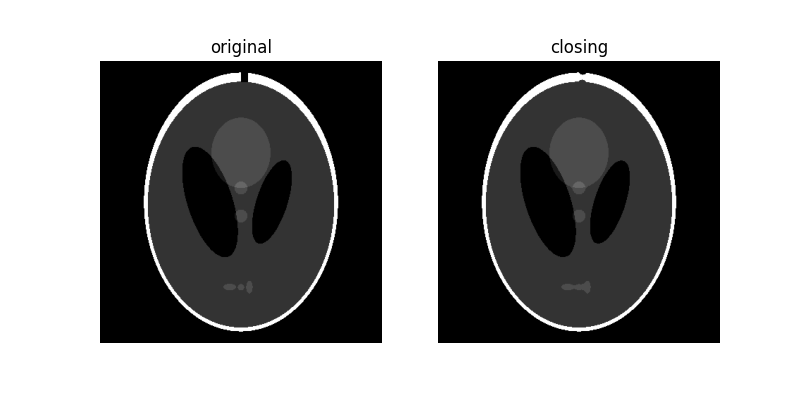
由於 閉運算 影像從膨脹操作開始,因此小於結構元素的黑暗區域會被移除。隨後的侵蝕操作可確保大於結構元素的黑暗區域保留其原始大小。請注意,底部的白色橢圓形如何因膨脹而連接,但其他黑暗區域保留其原始大小。另請注意,我們新增的裂縫大多已被移除。
白色頂帽#
影像的 white_tophat 定義為影像減去其形態學開運算。此操作會傳回小於結構元素的影像明亮斑點。
為了讓事情更有趣,我們將在影像中新增明亮和黑暗的斑點
phantom = orig_phantom.copy()
phantom[340:350, 200:210] = 255
phantom[100:110, 200:210] = 0
w_tophat = white_tophat(phantom, footprint)
plot_comparison(phantom, w_tophat, 'white tophat')
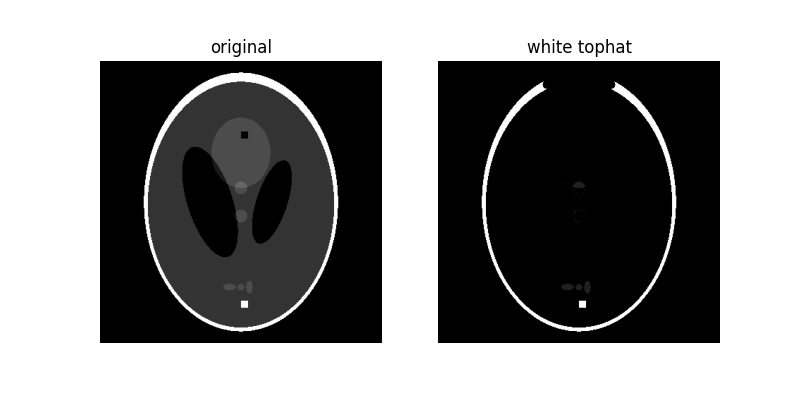

如您所見,由於 10 像素寬的白色正方形小於結構元素,因此被突出顯示。此外,橢圓形周圍的大部分細白色邊緣也被保留,因為它們小於結構元素,但頂部較厚的區域則消失了。
黑色頂帽#
影像的 black_tophat 定義為其形態學的閉運算減去原始影像。此操作會回傳影像中比結構元素小的暗點。
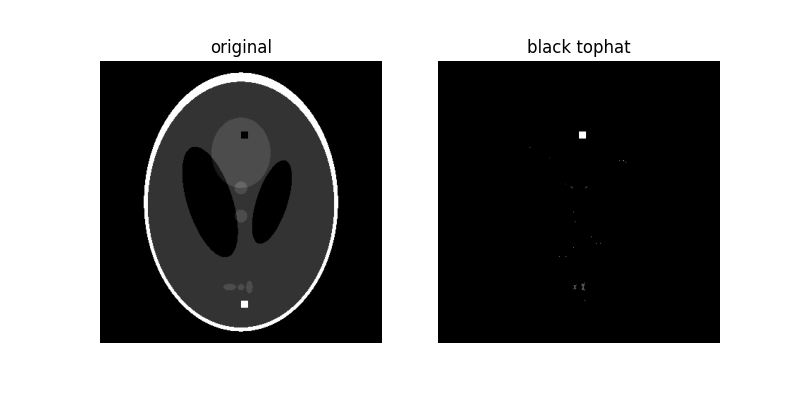

如您所見,由於 10 像素寬的黑色正方形小於結構元素,因此被突出顯示。
對偶性
您應該已經注意到,許多這些操作只是另一個操作的反向。這種對偶性可以總結如下:
侵蝕 <-> 膨脹
開運算 <-> 閉運算
白色頂帽 <-> 黑色頂帽
骨架化#
細化用於將二值影像中的每個連通組件縮減為單像素寬的骨架。重要的是要注意,這僅在二值影像上執行。
horse = data.horse()
sk = skeletonize(horse == 0)
plot_comparison(horse, sk, 'skeletonize')
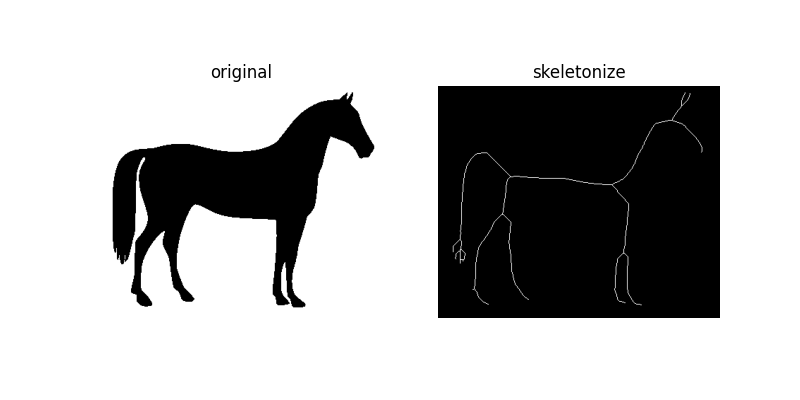
顧名思義,此技術透過連續應用細化來將影像細化為 1 像素寬的骨架。
凸包#
convex_hull_image 是包含在最小凸多邊形內的像素集合,該多邊形包圍輸入影像中的所有白色像素。再次注意,這也是在二值影像上執行的。
hull1 = convex_hull_image(horse == 0)
plot_comparison(horse, hull1, 'convex hull')
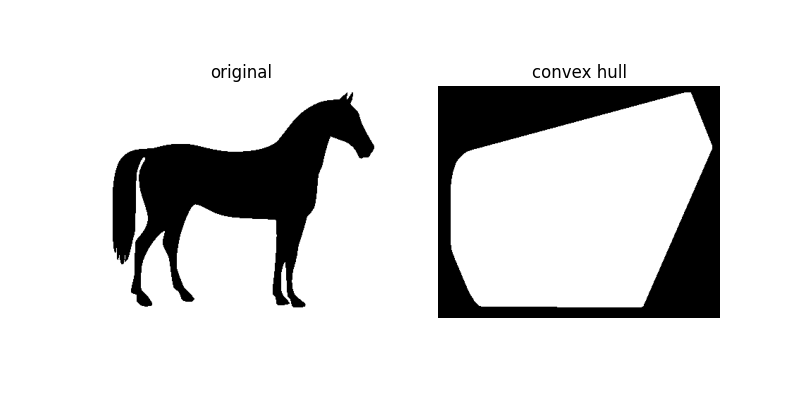
如圖所示,convex_hull_image 會給出覆蓋影像中白色或 True 的最小多邊形。
如果我們在影像中新增一個小顆粒,我們可以觀察凸包如何適應以包圍該顆粒。
horse_mask = horse == 0
horse_mask[45:50, 75:80] = 1
hull2 = convex_hull_image(horse_mask)
plot_comparison(horse_mask, hull2, 'convex hull')
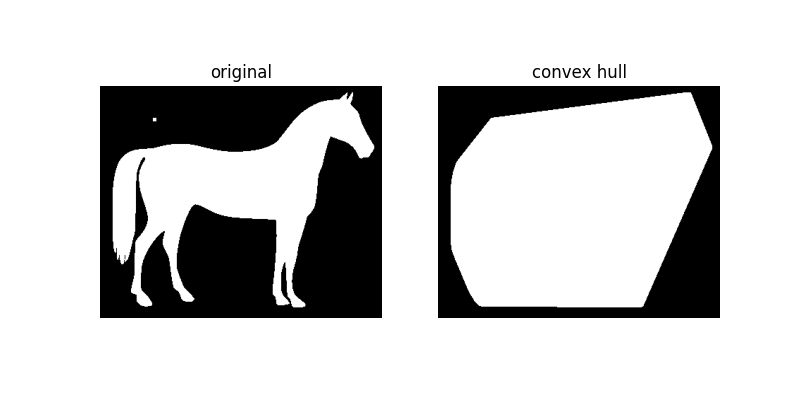
其他資源#
plt.show()
腳本的總執行時間: (0 分鐘 2.234 秒)
