注意
跳至結尾下載完整的範例程式碼。或通過 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
使用幾何變換#
在此範例中,我們將看到如何在影像處理的上下文中使用幾何變換。
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage import transform
基礎#
支援幾種類型的幾何變換:相似性、仿射、投影和多項式。有關可用變換類型的教學,請參閱單應性的類型。
幾何變換可以使用明確的參數(例如縮放、剪切、旋轉和平移)或變換矩陣來建立。
首先,我們使用明確的參數建立變換
tform = transform.SimilarityTransform(scale=1, rotation=math.pi / 2, translation=(0, 1))
print(tform.params)
[[ 6.123234e-17 -1.000000e+00 0.000000e+00]
[ 1.000000e+00 6.123234e-17 1.000000e+00]
[ 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 1.000000e+00]]
或者,您可以通過變換矩陣本身定義變換
matrix = tform.params.copy()
matrix[1, 2] = 2
tform2 = transform.SimilarityTransform(matrix)
然後,可以使用這些變換物件在來源和目的地座標系統之間應用正向和反向座標變換
[[6.123234e-17 3.000000e+00]]
[[ 0.000000e+00 -6.123234e-17]]
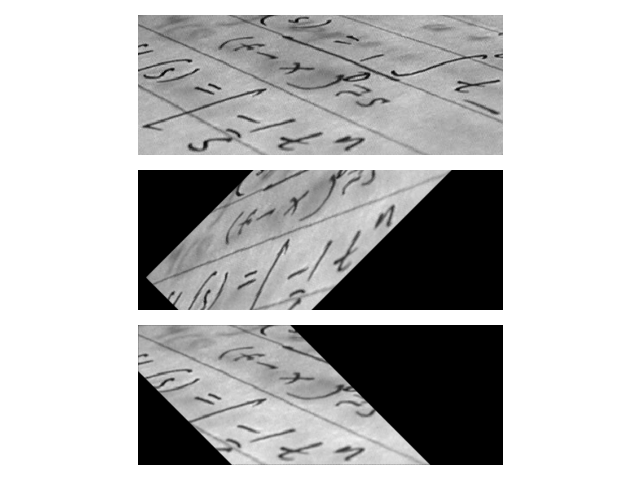
影像扭曲#
幾何變換也可以用於扭曲影像
text = data.text()
tform = transform.SimilarityTransform(
scale=1, rotation=math.pi / 4, translation=(text.shape[0] / 2, -100)
)
rotated = transform.warp(text, tform)
back_rotated = transform.warp(rotated, tform.inverse)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3)
ax[0].imshow(text, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].imshow(rotated, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[2].imshow(back_rotated, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
for a in ax:
a.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
參數估計#
除了上述基本功能外,您還可以使用最小二乘法估計幾何變換的參數。
這可以用於影像配準或校正等用途,其中您在兩個影像中有一組控制點或同源/對應點。
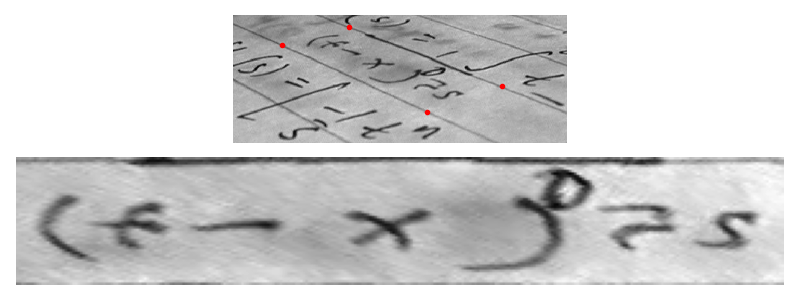
假設我們想辨識從非正面而是從某個角度拍攝的照片上的字母。在平面紙張表面的最簡單情況下,字母會以投影方式扭曲。簡單的匹配演算法將無法匹配此類符號。解決這個問題的一種方法是扭曲影像,以便消除扭曲,然後應用匹配演算法
text = data.text()
src = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 50], [300, 50], [300, 0]])
dst = np.array([[155, 15], [65, 40], [260, 130], [360, 95]])
tform3 = transform.ProjectiveTransform()
tform3.estimate(src, dst)
warped = transform.warp(text, tform3, output_shape=(50, 300))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, figsize=(8, 3))
ax[0].imshow(text, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].plot(dst[:, 0], dst[:, 1], '.r')
ax[1].imshow(warped, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
for a in ax:
a.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
上述估計依賴於對點位置的準確了解以及對其對應關係的準確選擇。如果點位置具有與之相關的不確定性,則可以提供權重,以便生成的變換優先考慮對權重最高的那些點進行準確擬合。當對應點不完全準確時,一種稱為 RANSAC 演算法 的替代方法非常有用。有關如何在 scikit-image 中使用此方法的深入描述,請參閱使用 RANSAC 的穩健匹配教學課程。
腳本總執行時間:(0 分鐘 0.763 秒)
